The Art Nouveau style of architecture
defined the transition between the 19th century and the 20th. It was
a global sensation that spawned numerous designers from around the
world. Hector Guimard, Charles Rennie, Mackintosh, and Victor Horta
were three prominent architects whose work helped foster this
movement.

The impetus behind Art Nouveau architectural design was to break
with tradition and explore newer and freer forms.
 Art
Nouveau's broad influence across architecture, design, and the
visual arts allowed architects to create total works of art, where
every element of a structure from its windows to its door handles to
its decorative flourishes could be harmonized to create an Art
Nouveau style.
Art
Nouveau's broad influence across architecture, design, and the
visual arts allowed architects to create total works of art, where
every element of a structure from its windows to its door handles to
its decorative flourishes could be harmonized to create an Art
Nouveau style.
Architects finished the interiors of their buildings as ornate as
their exteriors and decorated them with exquisite materials, custom
furnishings, and hand-painted wall treatments.
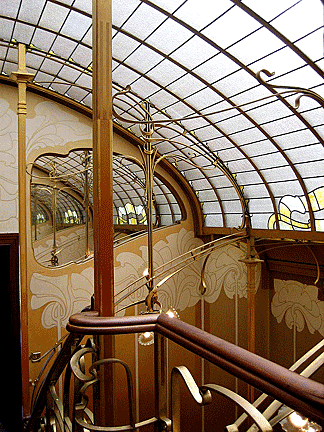
By opening up interior spaces, removing walls, and using skylights,
architects made the maximum use of light in their interior. Victor
Horta's residence-studio and other houses built by him had extensive
skylights, supported on curving iron frames. In the Hotel Tassel he
removed the traditional walls around the stairway, so that the
stairs became a central element of the interior design.
Art Nouveau architecture was a reaction against the eclectic styles
that dominated European architecture in the second half of the 19th
century. Architects used decoration, either ornamental or
sculptural. While faces of people, called mascarons, were ornament,
the use of people in different forms of sculpture was also common.

Characteristics of Art
Nouveau Architecture
 Art
Nouveau style is inspired by the natural world, characterized by
sinuous, sculptural, organic shapes, arches, curving lines, and
sensual ornamentation. Common motifs include stylized versions of
leaves, flowers, vines, insects, animals, and other natural
elements.
Art
Nouveau style is inspired by the natural world, characterized by
sinuous, sculptural, organic shapes, arches, curving lines, and
sensual ornamentation. Common motifs include stylized versions of
leaves, flowers, vines, insects, animals, and other natural
elements.
Decorative elements found on the inside and outside of buildings
include intricate mosaic work, stained and curved glass, and
decorative wrought iron.
Buildings and their interiors were asymmetrical. Architects
extensively employed arches and curved forms, including curving,
plant-like embellishments. They also used mosaics on both exteriors
and interiors. Stained and curved glass also became an integral part
of building designs.
Belgium
 Paul
Hankar and Victor Horta built the first Art Nouveau town houses in
Brussels—the Hankar House by Hankar in 1893 and the Hôtel Tassel by
Horta between 1892 and 1893. The theories of the French architect
Eugène Viollet-le-Duc inspired Hankar. With a goal to create a
synthesis of fine arts and decorative arts, he brought Adolphe
Crespin and Albert Ciamberlani to decorate the interior and exterior
of the Hankar House with sgraffito, or murals. Hankar decorated
stores, restaurants and galleries in completely original motifs.
Paul
Hankar and Victor Horta built the first Art Nouveau town houses in
Brussels—the Hankar House by Hankar in 1893 and the Hôtel Tassel by
Horta between 1892 and 1893. The theories of the French architect
Eugène Viollet-le-Duc inspired Hankar. With a goal to create a
synthesis of fine arts and decorative arts, he brought Adolphe
Crespin and Albert Ciamberlani to decorate the interior and exterior
of the Hankar House with sgraffito, or murals. Hankar decorated
stores, restaurants and galleries in completely original motifs.
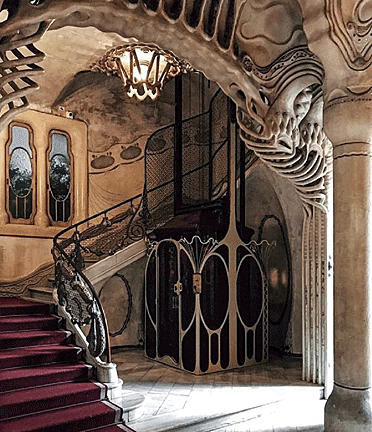
However, it was Horta who became one of the most influential
architects of early Art Nouveau, and his Hôtel Tassel was one of the
new style's landmarks. Horta worked as an assistant to Alphonse
Balat, architect to King Leopold II, constructing the monumental
iron and glass Royal Greenhouses of Laeken. Between 1892 and
 1893,
he designed the residence of a prominent Belgian chemist, Émile
Tassel, on a very narrow and deep site. The central focus of the
house was the open stairway, decorated with a curling wrought-iron
railing, and placed beneath a high skylight. He supported the floors
by slender iron columns like the trunks of trees and decorated the
mosaic floors and walls with delicate arabesques in floral and
vegetal forms. Horta built three more town houses, all with open
interiors, and all with skylights for maximum interior light: the
Hôtel Solvay, the Hôtel van Eetvelde, and the Maison & Atelier Horta.
1893,
he designed the residence of a prominent Belgian chemist, Émile
Tassel, on a very narrow and deep site. The central focus of the
house was the open stairway, decorated with a curling wrought-iron
railing, and placed beneath a high skylight. He supported the floors
by slender iron columns like the trunks of trees and decorated the
mosaic floors and walls with delicate arabesques in floral and
vegetal forms. Horta built three more town houses, all with open
interiors, and all with skylights for maximum interior light: the
Hôtel Solvay, the Hôtel van Eetvelde, and the Maison & Atelier Horta.
Henry van de Velde, born in Antwerp, was another founding figure of
Art Nouveau. Van de Velde's designs included the interior of his
residence, the Bloemenwerf, built in 1895. The Red House, the
residence of writer and theorist William Morris, the founder of the
Arts and Crafts Movement, inspired the exterior. Trained as a
painter, Van de Velde turned to illustration, then to furniture
design, and finally to architecture. For the Bloemenwerf, he created
the textiles, wallpaper, and silverware all of which matched the
style of the residence. Van de Velde went to Paris, where he
designed furniture and decoration for Sigfried Bing, whose Paris
gallery gave the style its name. He was also an early Art Nouveau
theorist, demanding the use of dynamic, often opposing lines.
A wave of decorative art accompanied the debut of Art Nouveau
architecture in Brussels. was accompanied by a wave of decorative
art in the new style. Important artists included Gustave Strauven,
who used wrought iron to achieve baroque effects on Brussels
facades; the furniture designer Gustave Serrurier-Bovy, known for
his highly original chairs and articulated metal furniture.

The Brussels International Exposition held in 1897 brought
international attention to the Art Nouveau style; Horta, Hankar, Van
de Velde, and Serrurier-Bovy, among others, took part in the design
of the fair, and Henri Privat-Livemont created the poster for the
exhibition.
France
 French
artists quickly noticed the new style. After visiting Horta's Hôtel
Tassel, Hector Guimard built the Castel Béranger, among the first
Paris buildings in the new style, between 1895 and 1898. Parisians
had been complaining of the monotony of the architecture of the
boulevards built under Napoleon III by Georges-Eugène Haussmann. The
Castel Beranger was a curious blend of Neo-Gothic and Art Nouveau,
with curving whiplash lines and natural forms.
French
artists quickly noticed the new style. After visiting Horta's Hôtel
Tassel, Hector Guimard built the Castel Béranger, among the first
Paris buildings in the new style, between 1895 and 1898. Parisians
had been complaining of the monotony of the architecture of the
boulevards built under Napoleon III by Georges-Eugène Haussmann. The
Castel Beranger was a curious blend of Neo-Gothic and Art Nouveau,
with curving whiplash lines and natural forms.
Parisians welcomed Guimard's original and picturesque style. The
Castel Béranger was chosen as one of the best new façades in Paris,
launching Guimard's career. Guimard was given the commission to
design the entrances for the new Paris Métro system, which brought
the style to the attention of the millions of visitors to the city's
1900 Exposition Universelle.
 In
Paris, Art Nouveau was a reaction to Georges-Eugène Haussmann’s
strict architectural restrictions imposed on building facades,
including a ban on bow windows until 1903. Art Nouveau architects
went to the opposite extreme, most notably in the houses of Jules
Lavirotte, which were essentially large works of sculpture,
completely covered with decoration. An important neighborhood of Art
Nouveau houses appeared in the French city of Nancy, around the
Villa Majorelle, designed by Henri Sauvage as a showcase for
Majorelle's furniture designs. between 1901 and 1902.
In
Paris, Art Nouveau was a reaction to Georges-Eugène Haussmann’s
strict architectural restrictions imposed on building facades,
including a ban on bow windows until 1903. Art Nouveau architects
went to the opposite extreme, most notably in the houses of Jules
Lavirotte, which were essentially large works of sculpture,
completely covered with decoration. An important neighborhood of Art
Nouveau houses appeared in the French city of Nancy, around the
Villa Majorelle, designed by Henri Sauvage as a showcase for
Majorelle's furniture designs. between 1901 and 1902.
Following the 1900 Exposition Universelle, the capital of Art
Nouveau moved to Paris. Jules Lavirotte built the most extravagant
residences in the new style. He covered the facades entirely with
ceramic sculptural decoration. The most flamboyant example is the
Lavirotte Building, at 29, avenue Rapp, built in 1901. Office
buildings and department stores featured high courtyards covered
with stained glass cupolas and ceramic decoration. The style became
especially popular in restaurants and cafés, including Maxim's at 3,
Rue Royale, and Le Train Bleu at the Gare de Lyon, built in 1900.
The City of Nancy in Lorraine became the other French capital of the
new style. In 1901, a group of artists founded the Alliance
Provinciale des Industries d'Art, also known as the L’École de
Nancy, dedicated to upsetting the hierarchy that put painting and
sculpture above the decorative arts. The architect Henri Sauvage
brought the new architectural style to Nancy with his Villa
Majorelle in 1902.
Germany
In Berlin Jugendstil was chosen for the construction of several
railway stations. The most notable is Bülowstraße by Bruno Möhring
(1900–1902), other examples are Mexikoplatz (1902–1904), Botanischer
Garten (1908–1909), Frohnau (1908–1910), Wittenbergplatz (1911–1913)
and Pankow (1912–1914) stations. Another notable structure of Berlin
is Hackesche Höfe (1906) which used polychrome glazed brick for the
courtyard facade.

Austria
Vienna became the center of a distinct variant of Art Nouveau, known
as the Vienna Secession. The movement took its name from the Munich
Secession established in 1892. A group of artists founded the Vienna
Secession in April 1897. They objected to the conservatism of the
Vienna Künstlerhaus, the official union of artists. The Secession
founded a magazine, Ver Sacrum, to promote their works in all media.
The architect Joseph Olbrich designed the domed Secession building
in the new style.
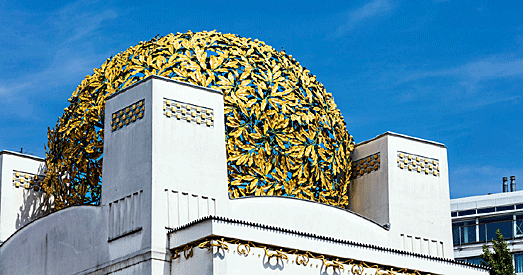
Otto Wagner, who joined the Succession early on, was the most
prominent architect of the Vienna Secession . His major projects
included several stations of the urban rail network, or Stadtbahn,
the Linke Wienzeile Buildings, consisting of Majolica House, the
House of Medallions and the house at Köstlergasse.
United States
Louis Sullivan of Chicago was an important figure in American Art
Nouveau architecture. Sullivan was a leading pioneer of American
modern architecture. He founded the Chicago School, and designed
some of the first skyscrapers. Sullivan firmly believed in the
concept of form follows function. While the function of his
buildings dictated their form, his decoration was an example of
American Art Nouveau. At the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition in
Chicago, most famous for the neoclassical architecture of its
renowned White City, he designed a spectacular Art Nouveau entrance
for the very functional Transportation Building.

